Dihydrocodeine Tablets 30 mg — Clinical Overview, Uses, and Safety Information
Overview
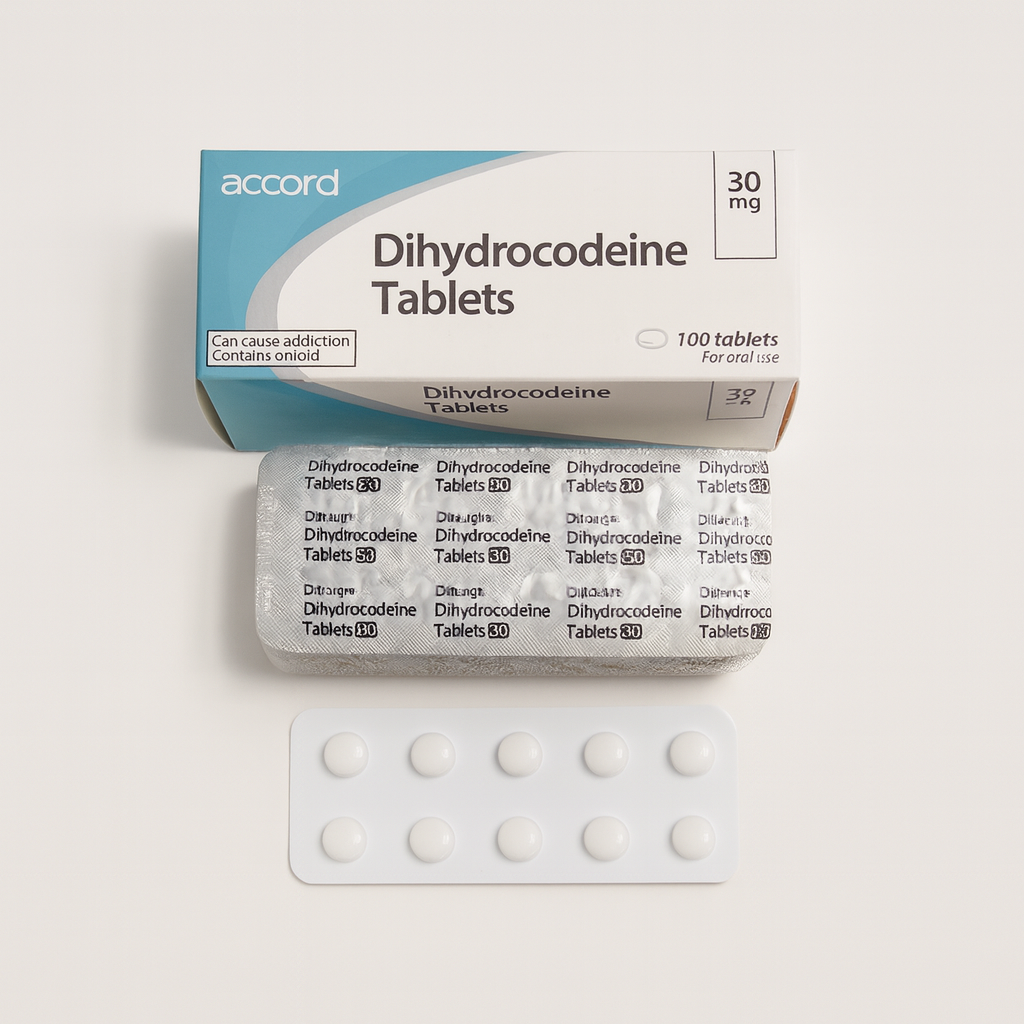
Dihydrocodeine Tablets 30 mg, manufactured by Accord Healthcare Ltd, contain dihydrocodeine tartrate, an opioid analgesic prescribed for the relief of moderate-to-severe pain.
Dihydrocodeine is a semi-synthetic derivative of codeine, first synthesized in the early 20th century, designed to provide stronger pain control while maintaining an acceptable safety profile when used responsibly under medical supervision.
The formulation complies with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) and British / European Pharmacopoeia standards, ensuring quality, consistency, and potency. Each tablet contains 30 mg dihydrocodeine tartrate for oral administration.
Pharmacological Profile
| Parameter | Description |
| Therapeutic class | Opioid analgesic |
| Active ingredient | Dihydrocodeine Tartrate 30 mg |
| Dosage form | Oral tablet |
| Manufacturer | Accord Healthcare Ltd |
| Indication | Moderate-to-severe pain unresponsive to non-opioid therapy |
| Regulatory status | Prescription-only (Controlled Drug in many regions) |
| Pack size | 100 tablets per carton |
Mechanism of Action
Dihydrocodeine acts primarily as a μ-opioid receptor agonist in the central nervous system (CNS) and to a lesser extent on κ- and δ-receptors.
When dihydrocodeine binds to these receptors, it reduces neuronal excitability and inhibits transmission of pain signals from the spinal cord to the brain.
At therapeutic doses it:
- Alters the perception of pain (raising the pain threshold)
- Reduces the emotional response to pain, improving tolerance
- Decreases cough reflex by direct action on the medullary centre
- May cause mild sedation and sense of calm useful for patients in persistent pain
The overall effect is a reduction in both intensity and awareness of pain, improving patient comfort and daily functioning.
Therapeutic Indications
Dihydrocodeine 30 mg is indicated for the relief of moderate or severe pain where non-opioid analgesics (e.g., paracetamol, NSAIDs) are insufficient.
Typical clinical situations include:
- Musculoskeletal pain – osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, back pain, sciatica, neuralgia.
- Post-operative pain – following surgery, dental extractions, or injury.
- Chronic pain syndromes – including cancer-related or neuropathic pain (as part of step-two therapy on the WHO analgesic ladder).
- Severe trauma pain – fractures, burns, or acute injuries where opioid therapy is justified.
- Cough suppression or dyspnoea relief – occasionally prescribed off-label under specialist care.
Use should always follow medical evaluation, with attention to underlying cause, pain severity, and individual patient tolerance.
Pharmacokinetics
| Parameter | Description |
| Absorption | Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration. |
| Onset of action | Within 30–60 minutes. |
| Peak plasma concentration | Typically 1.2–1.8 hours post-dose. |
| Bioavailability | Approximately 20–25 % (first-pass hepatic metabolism). |
| Metabolism | Hepatic, primarily via CYP2D6 → dihydromorphine (active metabolite). |
| Elimination half-life | 3–4 hours. |
| Excretion | Renal (urinary metabolites and unchanged drug). |
Dosage and Administration
Important: Dosage must be individualized. Always follow a doctor’s prescription and national prescribing guidelines.
Adults
- Typical dose: 30 mg every 4–6 hours as required for pain.
- Maximum daily dose: Usually not exceeding 240 mg/24 h unless specifically directed.
Elderly or Debilitated Patients
- Start with half the usual adult dose; titrate cautiously to effect.
Paediatric Use
- Not generally recommended below 12 years of age.
Administration Guidelines
- Tablets are taken orally with water, with or without food.
- Do not crush or chew unless advised (can affect absorption).
- Maintain consistent timing for sustained relief.
- Do not exceed the prescribed dose.
- Avoid concomitant alcohol or sedative medications.
Target Audience
- Adults with chronic or acute pain requiring opioid-level control.
- Post-operative patients transitioning from parenteral to oral analgesia.
- Palliative-care patients needing intermediate-strength opioids.
- Healthcare professionals seeking a step-two analgesic (between codeine and morphine).
Clinical Benefits
- Effective Analgesia: Rapid onset and reliable pain reduction.
- Intermediate Potency: Bridges the gap between mild analgesics and strong opioids.
- Cough Suppression: Beneficial secondary antitussive property.
- Improved Quality of Life: Allows mobility, sleep, and recovery from injury or surgery.
- Flexible Dosing: Tablets suitable for titration and combination therapy.
- Trusted Manufacturing: Accord Healthcare’s GMP-certified facilities ensure consistency.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to dihydrocodeine or other opioids.
- Acute respiratory depression.
- Asthma attack or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (severe).
- Head injury or raised intracranial pressure.
- Paralytic ileus or severe gastrointestinal obstruction.
- Acute alcoholism or concurrent use with monoamine-oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
- Children < 12 years.
Warnings and Precautions
- Dependence and Tolerance
- Repeated use may cause physical or psychological dependence.
- Limit duration of therapy to the shortest effective period.
- Respiratory Depression
- Monitor patients with compromised respiration (e.g., asthma, COPD).
- Driving and Machinery
- May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Avoid hazardous activities until the effect is known.
- Elderly and Hepatic Impairment
- Reduced metabolism; lower doses recommended.
- Concurrent CNS Depressants
- Alcohol, benzodiazepines, sedatives, or antihistamines can potentiate respiratory and sedative effects.
- Addiction Potential
- Prescribe only when necessary; reassess need periodically.
Adverse Effects
| Common | Less Common | Serious / Rare |
| Nausea | Constipation | Respiratory depression |
| Drowsiness | Vomiting | Hypotension |
| Dizziness | Dry mouth | Allergic reactions (rash, pruritus) |
| Headache | Light-headedness | Confusion or hallucination |
| Sweating | Miosis (pupil constriction) | Dependence or withdrawal symptoms |
Management: Most reactions are dose-related and may lessen with continued therapy or dose reduction.
Persistent or severe symptoms should prompt medical review.
Drug Interactions
- CNS depressants (alcohol, sedatives, hypnotics, antipsychotics, anesthetics): enhanced sedation/respiratory depression.
- Monoamine-oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs): contraindicated; may cause hypertensive crisis.
- CYP2D6 inhibitors (fluoxetine, paroxetine): altered metabolism and efficacy.
- Antihypertensives: increased risk of postural hypotension.
- Antidiarrheals / Antimuscarinics: additive constipation or urinary retention.
Overdose Management
Symptoms:
Extreme drowsiness, respiratory depression, cyanosis, pinpoint pupils, hypotension, bradycardia, coma.
Treatment:
- Maintain airway and ventilation.
- Administer Naloxone (opioid antagonist) intravenously if indicated.
- Supportive measures (oxygen, IV fluids).
- Continuous monitoring until full recovery.
Use in Specific Populations
| Group | Recommendation |
| Pregnancy | Use only if benefits outweigh risks; may cause neonatal withdrawal or respiratory depression. |
| Lactation | Small amounts excreted in breast milk; avoid or monitor infant closely. |
| Elderly | Use lower doses; increased sensitivity to opioid effects. |
| Renal / Hepatic impairment | Dose adjustment required; monitor for accumulation. |
| Children | Not recommended < 12 years; caution in adolescents. |
Storage and Handling
- Store below 30 °C, protected from moisture and direct sunlight.
- Keep tablets in the original blister pack until administration.
- Keep out of reach of children.
- Dispose of unused tablets through a licensed take-back or pharmacy return program.
Patient Counselling Points
Healthcare professionals should advise patients to:
- Take medicine exactly as prescribed — never exceed the dose.
- Avoid alcohol and sedatives during treatment.
- Report breathing difficulties, confusion, or excessive drowsiness immediately.
- Prevent constipation through dietary fibre and hydration.
- Do not stop suddenly after long-term use — gradual tapering prevents withdrawal.
- Store securely to prevent misuse or accidental ingestion.
Problem Addressed
Persistent or moderate-to-severe pain can severely impact daily functioning, sleep quality, and psychological health.
When non-opioid medications are inadequate, an intermediate opioid such as dihydrocodeine provides a balanced approach to pain relief.
Dihydrocodeine modifies both the sensory and emotional components of pain perception. It allows patients to regain control over mobility, rest, and productivity — essential elements of recovery and rehabilitation.
By adhering to prescribed doses and duration, patients can benefit from effective analgesia while minimizing the risks associated with opioid therapy.
Desired Outcomes and Clinical Benefits
- Reliable pain control with manageable side-effect profile.
- Improved functional ability in chronic pain conditions.
- Enhanced sleep and psychological wellbeing by reducing pain-related distress.
- Better tolerance than stronger opioids in many patients.
- Stepwise escalation option on the WHO analgesic ladder, offering flexibility in therapy planning.
Legal and Regulatory Notice
This content is provided solely for educational and informational purposes.
Dihydrocodeine Tablets 30 mg are prescription-only and regulated as controlled substances in many jurisdictions.
They must be dispensed by a licensed pharmacist and used under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional.
The information herein does not constitute medical advice or product promotion.
Always consult a doctor or pharmacist before initiating, changing, or discontinuing any opioid therapy.
Conclusion
Dihydrocodeine Tablets 30 mg (Accord Healthcare) play a valuable role in step-two pain management strategies, bridging mild and strong opioids.
Their rapid onset, balanced potency, and established efficacy make them a dependable choice for clinicians managing moderate-to-severe pain.
Used responsibly within medical and regulatory guidelines, dihydrocodeine provides meaningful relief, improved mobility, and enhanced quality of life for patients living with persistent pain.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.