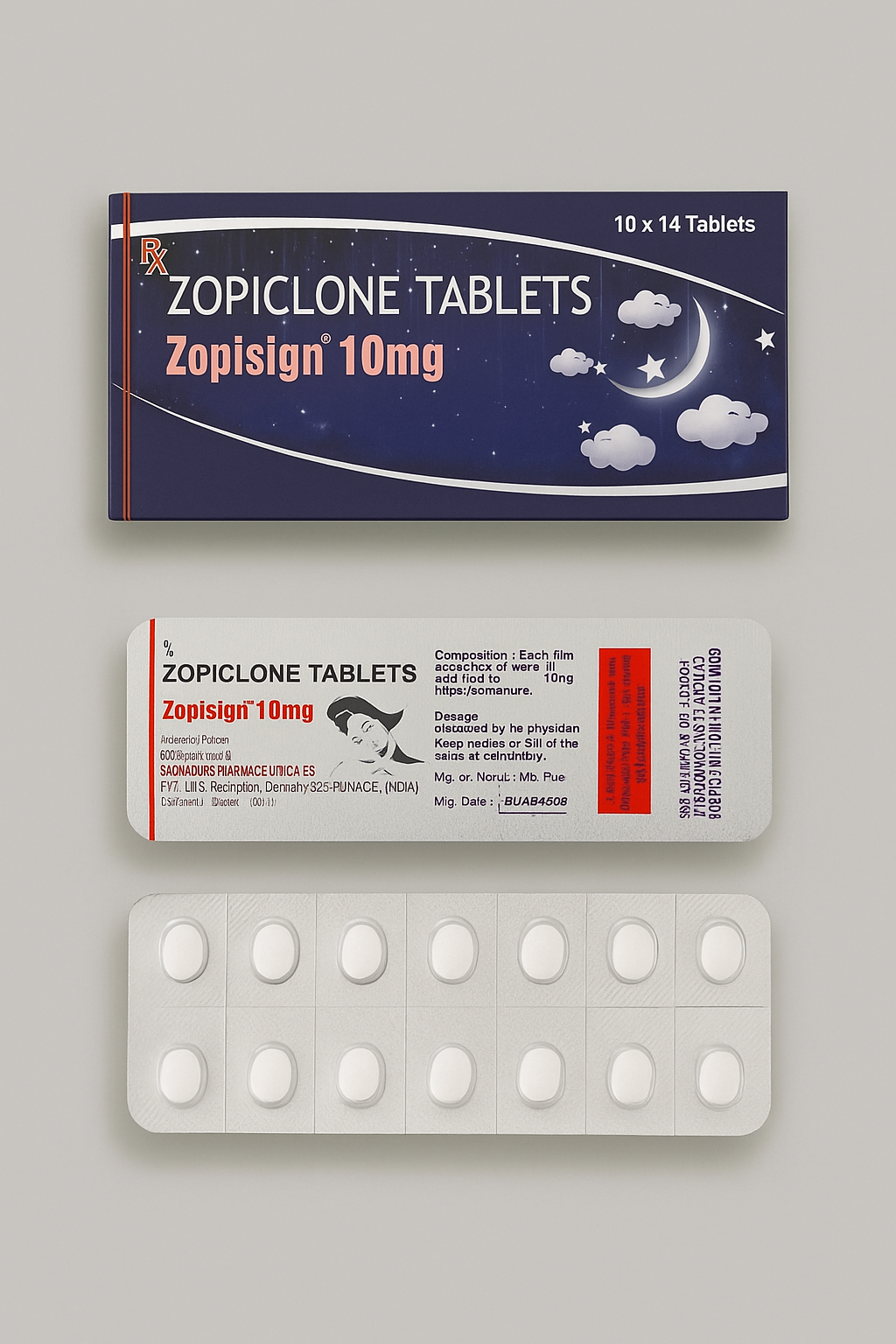
Zopisign 10mg contains the active ingredient Zopiclone, a non-benzodiazepine hypnotic agent used in the short-term management of insomnia and sleep disorders. Belonging to the cyclopyrrolone class, Zopiclone acts as a central nervous system (CNS) depressant that enhances the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmission, thereby promoting sleep induction and maintenance.
Zopisign is indicated for transient, situational, and chronic insomnia in adults, especially where sleep initiation, continuity, or quality is compromised. The product provides fast onset, effective duration, and reduced residual daytime sedation, distinguishing it from older hypnotics.
Manufactured by Soanadurs Pharmaceutica Pvt. Ltd., India, Zopisign 10mg Tablets are a reliable, clinically proven formulation designed for healthcare professionals seeking precise dosing, predictable pharmacokinetics, and strong patient tolerability profiles.
Pharmacological Classification
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Generic Name | Zopiclone |
| Brand Name | Zopisign 10mg |
| Active Ingredient | Zopiclone 10 mg per tablet |
| Pharmacological Class | Cyclopyrrolone derivative / Non-benzodiazepine hypnotic |
| Therapeutic Category | Sedative-hypnotic / CNS depressant |
| Dosage Form | Oral tablet |
| Route of Administration | Oral |
| Manufacturer | Soanadurs Pharmaceutica (India) |
| Packaging | 10 × 14 tablets (140 tablets) |
| Prescription Category | Rx (Schedule H) |
Mechanism of Action
Zopiclone, the active molecule in Zopisign 10mg, acts selectively on GABA-A receptors at the benzodiazepine recognition site, distinct from classical benzodiazepines. It enhances GABA-mediated chloride ion influx into neurons, leading to neuronal hyperpolarization and suppression of cortical excitability.
Unlike benzodiazepines, Zopiclone binds with high affinity to the omega-1 (α1) subunit of the GABA-A receptor, thereby inducing sedation and hypnosis without pronounced anxiolytic or anticonvulsant effects.
Neuropharmacologic Pathway
-
GABA Potentiation: Increases GABAergic transmission at inhibitory synapses.
-
Cortical Inhibition: Reduces neuronal firing in the reticular activating system.
-
Sleep Induction: Decreases sleep latency (time to fall asleep).
-
Sleep Maintenance: Reduces night-time awakenings and prolongs total sleep duration.
Therapeutic Indications
Zopisign 10mg is clinically indicated for the short-term management of insomnia where sleep initiation or maintenance is difficult. Specific uses include:
-
Transient Insomnia:
-
Caused by situational stress (travel, jet lag, emotional upset, shift work).
-
-
Short-term Insomnia:
-
Associated with acute medical or psychiatric conditions.
-
-
Chronic Insomnia:
-
When sleep disorders persist and behavioral interventions alone are insufficient.
-
-
Adjunctive Therapy:
-
As part of a comprehensive treatment plan for anxiety or depressive disorders presenting with sleep disturbance.
-
Pharmacokinetics
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Absorption | Rapidly and completely absorbed after oral administration. |
| Bioavailability | Approximately 75–80%. |
| Time to Peak Plasma (Tmax) | 1.5–2 hours post-dose. |
| Protein Binding | About 45%. |
| Metabolism | Extensively hepatic, mainly by CYP3A4 and CYP2C8 isoenzymes. |
| Elimination Half-Life (t½) | 4.5–6.5 hours (may be prolonged in elderly or hepatic impairment). |
| Excretion | 75% renal (metabolites), 16% fecal. |
| Onset of Action | 20–30 minutes. |
| Duration of Effect | 6–8 hours. |
Clinical Implication
The short half-life and rapid clearance minimize next-day sedation, making Zopisign suitable for patients requiring alertness during daytime.
Dosage and Administration
Note: Dosage must be individualized based on age, clinical response, and comorbid conditions. Always administer immediately before bedtime.
Standard Adult Dose
-
Usual dose: 7.5 mg to 10 mg once daily at bedtime.
-
Maximum dose: 10 mg per day.
Elderly or Debilitated Patients
-
Initial dose: 3.75 mg once daily.
-
Adjust based on tolerability and efficacy.
Hepatic Impairment
-
Reduce dosage to 3.75 mg to minimize accumulation risk.
Renal Impairment
-
Mild to moderate: No dosage adjustment usually required.
-
Severe: Caution advised due to metabolite accumulation.
Duration of Therapy
-
Short-term use only: 2 to 4 weeks, including dose tapering.
-
Long-term administration increases the risk of dependence and tolerance.
Target Audience
-
Adults (≥18 years) with insomnia or poor sleep quality.
-
Healthcare professionals managing patients with sleep initiation or maintenance difficulties.
-
Elderly patients requiring low-dose hypnotics.
-
Patients with anxiety-related sleep issues unresponsive to behavioral interventions.
Not indicated for pediatric populations, pregnant women, or breastfeeding mothers.
Clinical Benefits
-
Rapid Onset of Sleep: Zopisign promotes sleep within 20–30 minutes post-ingestion.
-
Improved Sleep Duration: Increases total sleep time by reducing nocturnal awakenings.
-
Enhanced Sleep Quality: Promotes Stage 2 and slow-wave sleep with minimal REM suppression.
-
Minimal Hangover Effect: Short elimination half-life ensures alertness next morning.
-
Better Tolerability: Lower incidence of muscle relaxation, ataxia, or amnesia compared to benzodiazepines.
-
Predictable Pharmacokinetics: Suitable for both intermittent and continuous short-term therapy.
-
Reduced Risk of Dependence: When used under appropriate medical supervision and for limited duration.
Problem Addressed — Insomnia
Insomnia is a widespread sleep disorder affecting millions worldwide. It manifests as:
-
Difficulty initiating sleep.
-
Frequent nocturnal awakenings.
-
Early morning awakening with inability to resume sleep.
-
Non-restorative or poor-quality sleep.
Consequences of Untreated Insomnia
-
Fatigue, irritability, and daytime drowsiness.
-
Impaired concentration and memory.
-
Increased cardiovascular and metabolic risk.
-
Decreased occupational performance.
Zopisign 10mg targets the neurochemical imbalance responsible for disturbed sleep. By enhancing GABAergic inhibition, it helps restore normal sleep architecture, reducing sleep latency and improving overall restfulness.
Contraindications
-
Hypersensitivity to Zopiclone or any tablet component.
-
Myasthenia gravis.
-
Severe hepatic impairment.
-
Severe sleep apnea syndrome.
-
Acute or severe respiratory insufficiency.
-
History of drug or alcohol dependence.
Warnings and Precautions
-
Dependence and Withdrawal:
-
Risk increases with prolonged use (>4 weeks), high doses, or history of substance misuse.
-
-
Rebound Insomnia:
-
Temporary sleep disturbances may recur upon discontinuation; taper gradually.
-
-
Amnesia and Psychomotor Impairment:
-
May occur if the patient does not get a full night’s sleep (≥7 hours).
-
-
Complex Sleep Behaviors:
-
Rare reports of sleep-driving, sleep-eating, or engaging in activities while not fully awake.
-
-
CNS Depression:
-
Concomitant alcohol or sedative use enhances depressive effects.
-
-
Hepatic and Renal Dysfunction:
-
Dose adjustment necessary; monitor liver and kidney parameters.
-
-
Elderly Patients:
-
Use lowest effective dose due to increased fall risk and prolonged half-life.
-
Adverse Reactions
| System / Organ | Adverse Effects | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| CNS | Drowsiness, dizziness, headache, confusion | Common |
| Gastrointestinal | Dry mouth, bitter taste, nausea | Common |
| Psychiatric | Nightmares, agitation, hallucinations (rare) | Uncommon |
| Respiratory | Mild respiratory depression (high doses) | Rare |
| Neuromuscular | Ataxia, fatigue | Common |
| Dermatologic | Rash, pruritus | Rare |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | Rebound insomnia, anxiety, tremors | Possible with abrupt cessation |
Most side effects are dose-related and transient, resolving within 24–48 hours after discontinuation.
Drug Interactions
| Drug / Substance | Interaction Type | Clinical Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | Additive CNS depression | Avoid concomitant use |
| CNS Depressants (benzodiazepines, opioids) | Synergistic sedation | Caution, dose adjustment required |
| CYP3A4 Inhibitors (ketoconazole, erythromycin) | ↑ Zopiclone plasma levels | Consider dose reduction |
| CYP3A4 Inducers (rifampicin, phenytoin, carbamazepine) | ↓ Plasma concentration | May reduce hypnotic efficacy |
| Antidepressants (SSRIs, tricyclics) | Additive sedative effect | Monitor for CNS depression |
| Opioids | Increased risk of respiratory depression | Use lowest effective doses |
Storage and Stability
-
Store below 30°C, protected from light and moisture.
-
Keep in the original blister pack until use.
-
Shelf life: 24 months from manufacturing date.
-
Keep out of reach of children.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.